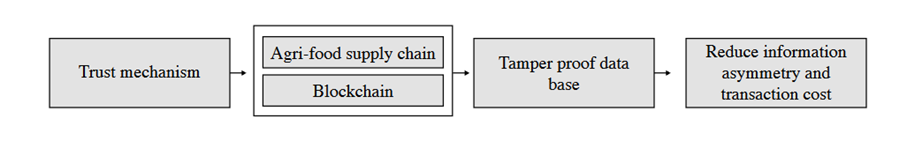
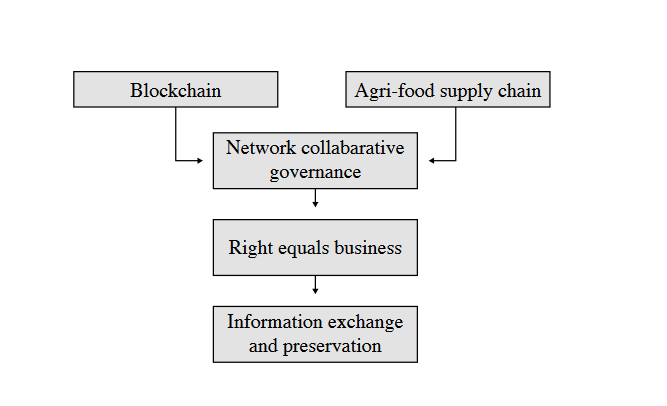
Blockchain technology connects multiple entities of the agri-food supply chain, forming a unified database
CASE STUDIES: EXAMPLE 1
- - Case Study of a Traditional Bakery: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9410538
- - Case Study in China
- https://www.wageningenacademic.com/doi/epdf/10.22434/IFAMR2019.0152?role=tab
- - Uncovering the potential of blockchain in the agri-food supply chain
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0923474822000303
- Case one1: blockchain-based poultry farming ecosystem – ‘Bu Bu Chicken’ project
- The 'Bu Bu Chicken' project by Zhong An Technology utilizes special technology like sensors and a secure database called 'An Chain Cloud' to track the chicken's journey from the farm to the consumer's plate.
- Sensors placed on the chicken collect data about its location and the conditions it's raised in, which is then stored securely in a database.
- Consumers can access this data through a mobile app, which provides detailed information about the chicken's origin, handling, and transportation.
- To ensure the reliability of the information, multiple parties agree on it using a special system, increasing trust among consumers.
- Zhong An Technology collaborates with farmers, delivery companies like SF EXPRESS, processing plants, and online stores such as JD.com to implement the project.
- The use of blockchain technology helps in tracking the chicken's journey from birth to sale, facilitating transparency and reliability.
- 'Bu Bu Chicken' is priced at $33 and is available on platforms like SF Best Choice and JD.com.
- Currently, Zhong An Technology works with over 200 farms across China and aims to expand to 2,500 farms by 2020.
- Zhong An also offers financial services such as insurance and loans to farmers and businesses involved in the project, leveraging data from the blockchain system to ensure affordability and accessibility.
(Fu et al., 2020)
CASE STUDIES: EXAMPLE 2
Case two2: ‘Shan Liang Taste’ – the agri-food supply chain system under the blockchain environment
- Shan Liang Taste combines Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and big data to develop an agri-food supply chain management platform.
- They digitize the assets of Beidahuang Farm Group, breaking down its grain supply chain into 1,639 business nodes across 3 farms, 9 management districts, and 33 workstations.
- By adopting standardized, large-scale, and mechanized production methods, Shan Liang Taste creates an autonomous agricultural system powered by intelligent equipment and blockchain.
- Various IoT devices installed on equipment automatically collect data such as time, location, planting details, and management data, which is uploaded to the blockchain system to ensure authenticity.
- Participants in the grain supply chain record transaction information on the blockchain system, ensuring transaction security and comprehensive data mapping.
- Shan Liang Taste develops various apps within the blockchain platform to manage the grain supply chain effectively:
- Shan Liang Blockchain Food Tickets app issues tradable and collateralized digital planting orders corresponding to land.
- Shan Liang Blockchain Order via WeChat allows customers to book land for rice production, with orders costing $1,150 for 1 mu land.
- Shan Liang Smart Contract app provides supply chain order contracts, effectively solving trust issues.
- Shan Liang Steward app standardizes production services including breeding, procurement of agricultural materials, and production planning.
- Shan Liang Finance app, in collaboration with financial institutions, offers new financial services to supply chain partners based on blockchain data assets and trading data.
- Shan Liang Taste also collaborates with various institutions for quality inspection and technical support, further enhancing the quality of grain production.
- Overall, Shan Liang Taste revolutionizes the traditional hierarchical model of the agri-food supply chain, leveraging technology to upgrade industrial processes and ensure grain quality from the source.
Please rephrase it in easy language
(Fu et al., 2020)
CASE STUDIES: SUMMARY
Blockchain and agri-food supply chain are coupled in trust mechanism
Blockchain and agri-food supply chain are coupled in management structure
(Fu et al., 2020)